This post lists all the log files related to SCCM CMG. You can use these SCCM CMG log files for troubleshooting issues related to the Cloud Management Gateway.
When you set up a SCCM CMG, you must know the CMG log files that will help you troubleshoot issues. The majority of the CMG log files are kept on an Azure server, with some being stored on site servers.
Despite the fact that there aren’t many CMG log files available, you still need to know where they are in order to troubleshoot CMG issues. They are either located on site server or on Azure server. Read how to Fix SCCM CMG Failed to Sign in to Azure Error.
In my previous post I covered on steps to enable remote desktop in CMG. If you enable the remote desktop in SCCM CMG, you can access the CMG log files easily. To set up SCCM CMG from scratch, refer to this step-by-step guide – https://www.prajwaldesai.com/setup-sccm-cloud-management-gateway/
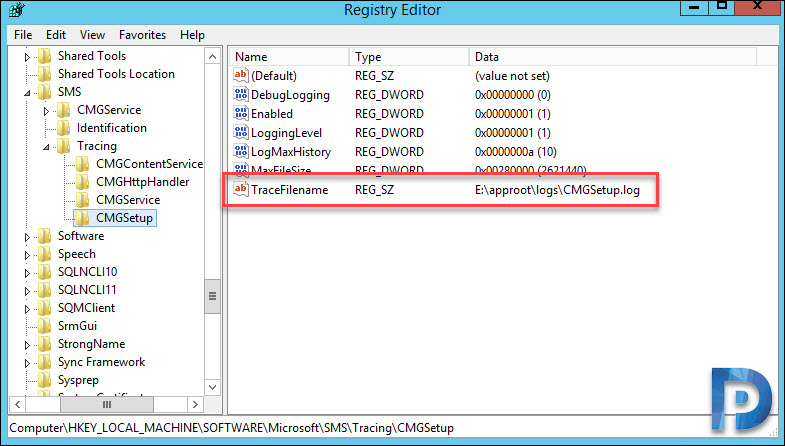
The registry on CMG VM holds the location details of the log files. You have to RDP the CMG VM to access the log files. When you log in to CMG virtual machine, navigate to HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\SMS\Tracing\CMGSetup. The registry key TraceFilename show the actual location CMG log files – E:\approot\logs\CMGSetup.log.
CMGSetup.log, CMGHttpHandler.log, CMGService.log – These are local Configuration Manager log files that cloud service manager syncs from Azure storage every five minutes. The cloud management gateway pushes logs to Azure storage every five minutes.
- For troubleshooting deployments, use CloudMgr.log and CMGSetup.log
- For troubleshooting service health, use CMGService.log and SMS_Cloud_ProxyConnector.log.
- For troubleshooting client traffic, use CMGService.log and SMS_Cloud_ProxyConnector.log.
Also Read: Fix ConfigMgr CMG Stuck in Starting State
CMG Logs synchronized from Azure
These are local Configuration Manager log files that cloud service manager syncs from Azure storage every five minutes. The cloud management gateway pushes logs to Azure storage every five minutes. So, the maximum delay is 10 minutes. The verbose switches affect both local and remote logs. The actual file names include the service name and role instance identifier. For example, CMG-ServiceName-RoleInstanceID-CMGSetup.log. These log files are synced, so you don’t need to RDP to the cloud management gateway to obtain them, and that option isn’t supported.
Recommended Article: ConfigMgr CMG Error – The remote name could not be resolved
SCCM CMG Log Files for Troubleshooting
The table below includes information about each SCCM CMG log files name, location, and description.
| CMG Log File Name | Description | Log File Location |
|---|---|---|
| SMS_Cloud_ProxyConnector.log | Records details about setting up connections between the cloud management gateway service and the cloud management gateway connection point. | This log file is located on site system server – C:\Program Files\Microsoft Configuration Manager\Logs |
| CloudMgr.log | This file logs details related to cloud management gateway service, ongoing service status, and all the data associated with the service. | On site server – C:\Program Files\Microsoft Configuration Manager\Logs |
| CMGContentService.log | This log records the details of the service when you enable a CMG to also serve content from Azure storage. | %approot%\logs on your Azure server |
| CMGService.log | Records details about the cloud management gateway (CMG) service core component in Azure. | %approot%\logs on your Azure server |
| CMGHttpHandler.log | You see this log file only if you are using version 1802. This is because in SCCM 1806, this log has been removed. The component functionality is merged into the CMG service component. Therefore see the CMGService.log instead. | %approot%\logs on your Azure server |
| CMGSetup.log | Records details about the second phase of the cloud management gateway deployment (local deployment in Azure). | %approot%\logs on your Azure server |













Anything logged client side? My clients aren’t talking to the CMG and I can’t figure out why.
cuando tengo implementado IBCM e implemento CMG como obligo al cliente a que use CMG en lugar de IBCM.
How does SCCM tool decide Client is on the internet and switch to CMG ?
The logs on the site server could be in a different location if SCCM was not installed to the default location on the C drive. To find the logs, the path would be “<SCCM installation directory\Logs" such as "E:\Microsoft Configuration Manager\Logs" or they could be found by using the SMS_Sitecode share such as "\\CMServer\SMS_USA\Logs"
Agreed.